Adjudication
The Adjudication component is a crucial part of the annotation tool. It plays a significant role in facilitating agreement among annotators, ultimately leading to a high-quality, consensus-driven annotated dataset.
The component consists of several features:
Sorting, Filtering, and Pagination: This feature enables efficient navigation and management of dataset items. Items can be sorted based on agreement scores, filtered via text search or flags, and neatly organised through pagination.
Overview: This provides a quick summary of each dataset item, including details such as agreement scores, flags applied, save states, and the last updated time.
Main View and Annotator Selector: The Main View exhibits the annotations applied to each dataset item, while the Annotator Selector allows for dynamic viewing options. Depending on the selection, one can view annotations from all annotators, a single annotator, or a comparison between two annotators.
Adjudication plays a pivotal role in the process of dataset annotation by enabling project managers to identify areas of strong agreement or discord among annotators, fostering collaborative improvement and ensuring the production of a high-quality annotated dataset.
1. Sorting, Filtering and Pagination Features
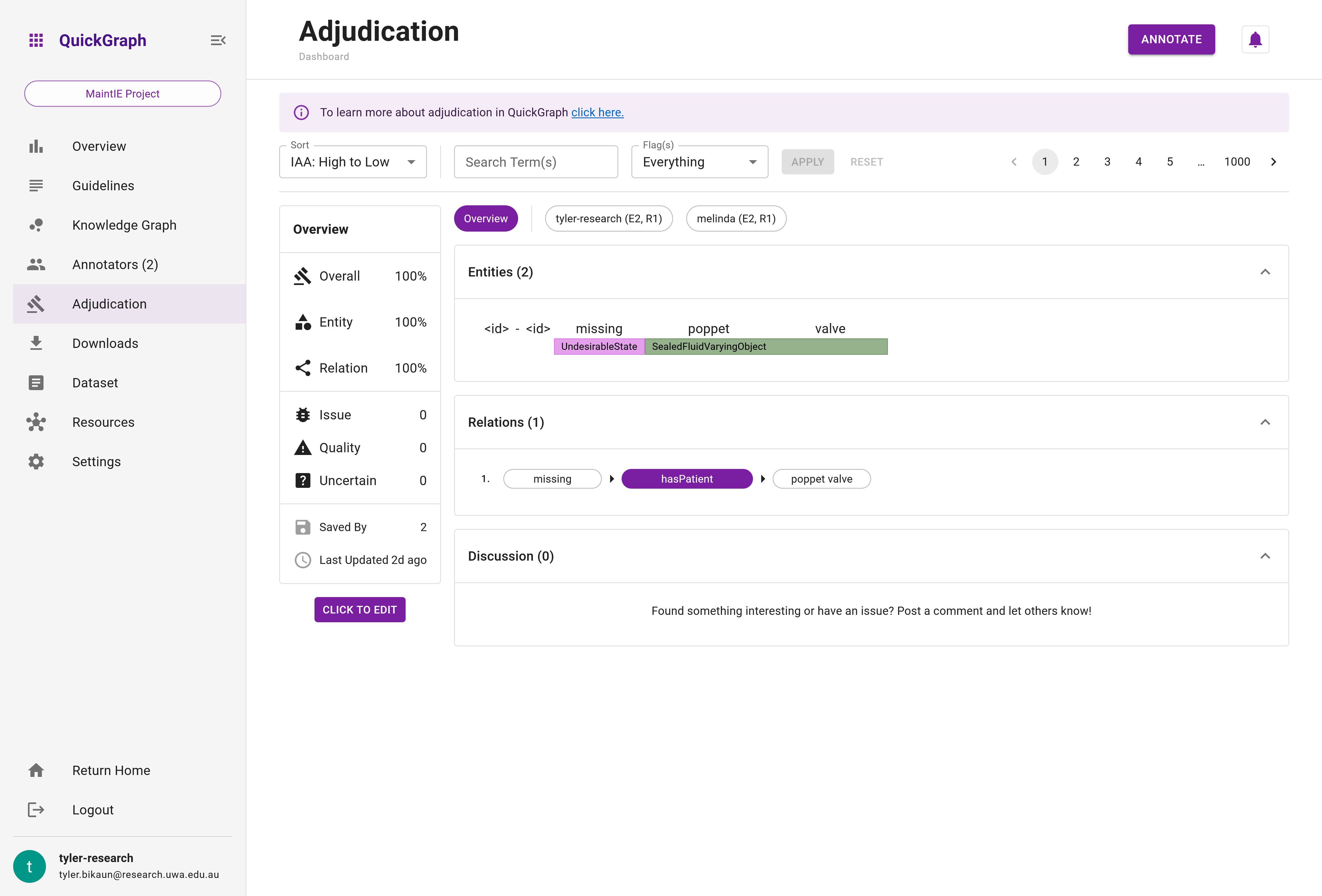
The adjudication interface allows you to sort, filter, and paginate through dataset items for efficient adjudication. See Figure 2 for an overview of these features.

Sorting
You can sort dataset items according to their interannotator agreement scores. The sorting options include Low to High and High to Low (default).
If your project is entity annotation only, the overall agreement score will reflect entity agreement only.
Filters
The adjudication interface provides two filters to assist you in finding relevant dataset items: a free text search and flag-based filtering.
- Free text search: This filter allows you to search within the content of the dataset items. Items that match your search terms will be displayed.
- Flag(s) filter: You can filter dataset items based on flags assigned by annotators. The available flags are
no flags,issue,quality,uncertain, with the default setting beingeverything.
Pagination
The pagination feature enables you to navigate through dataset items systematically. You can move through pages by clicking the page numbers or using the left and right arrows.
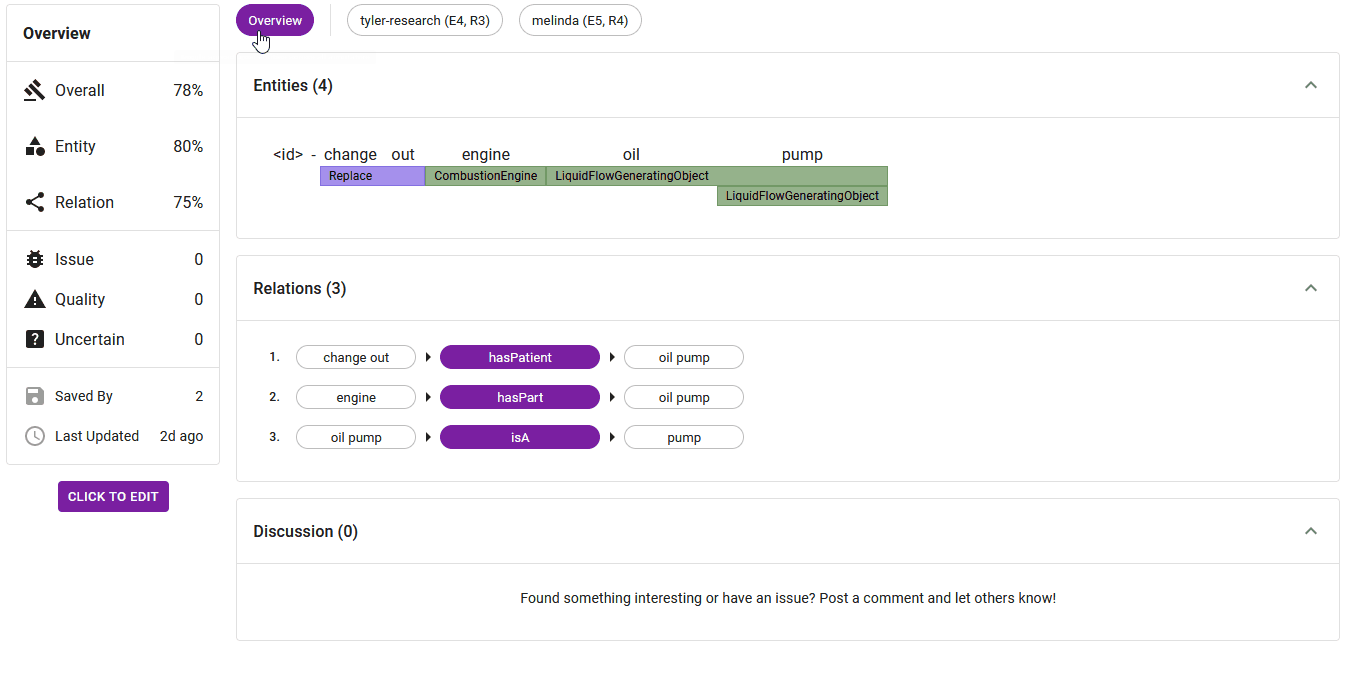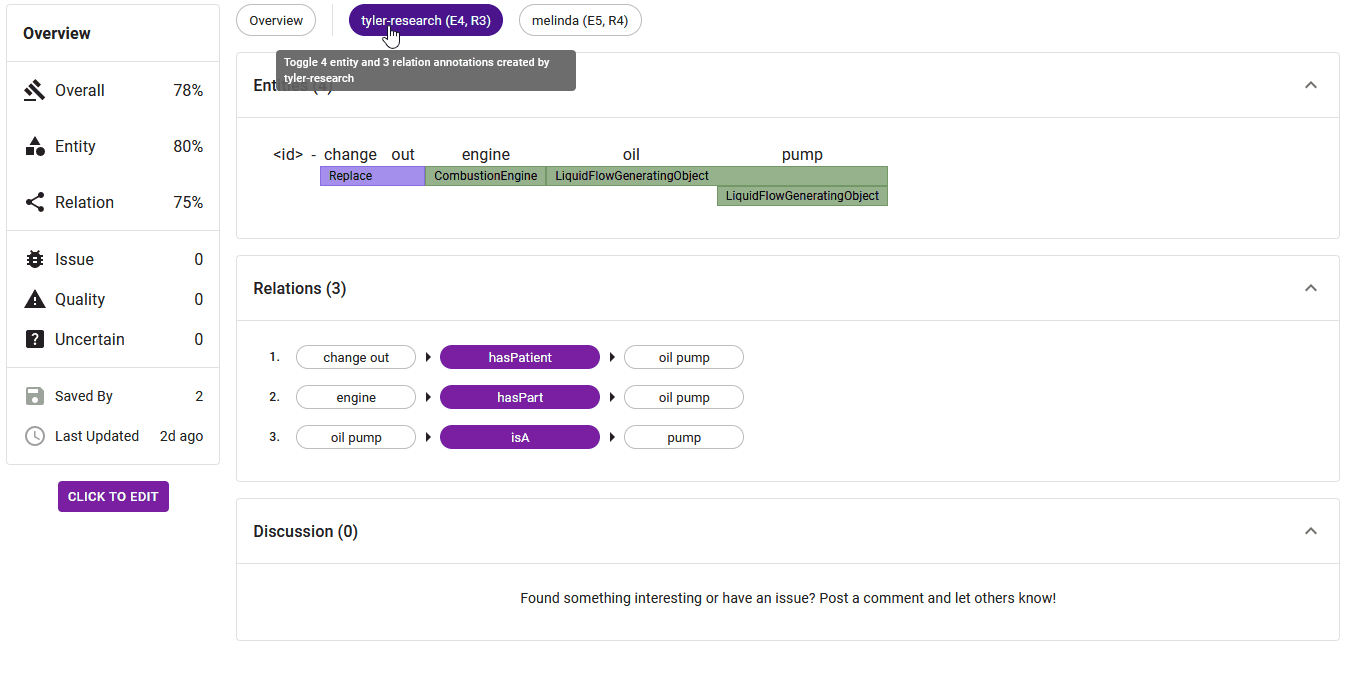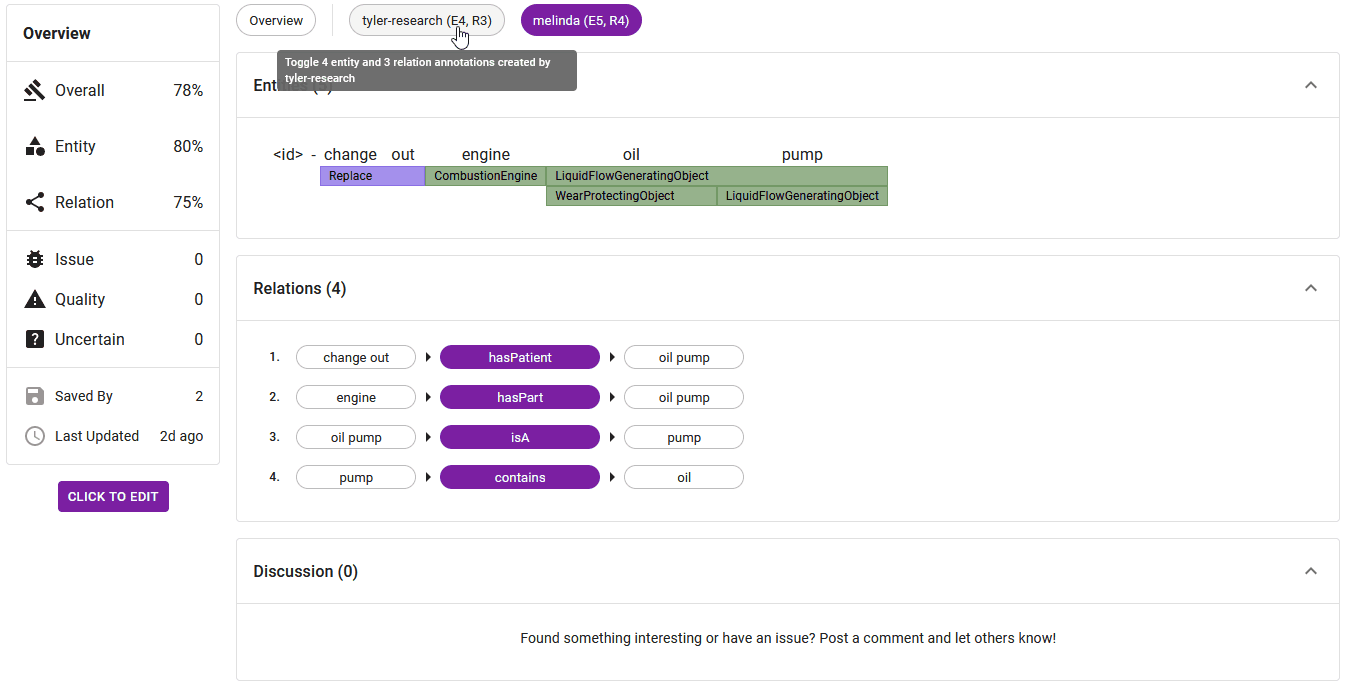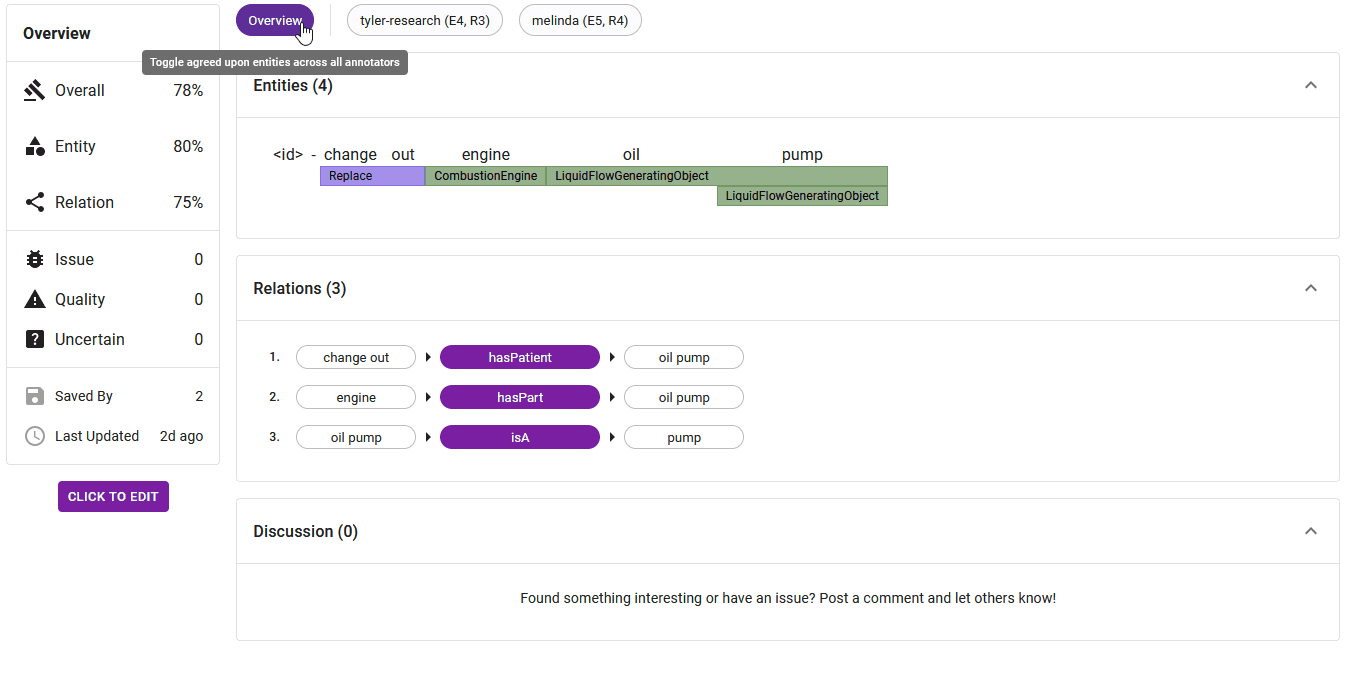
2. Overview
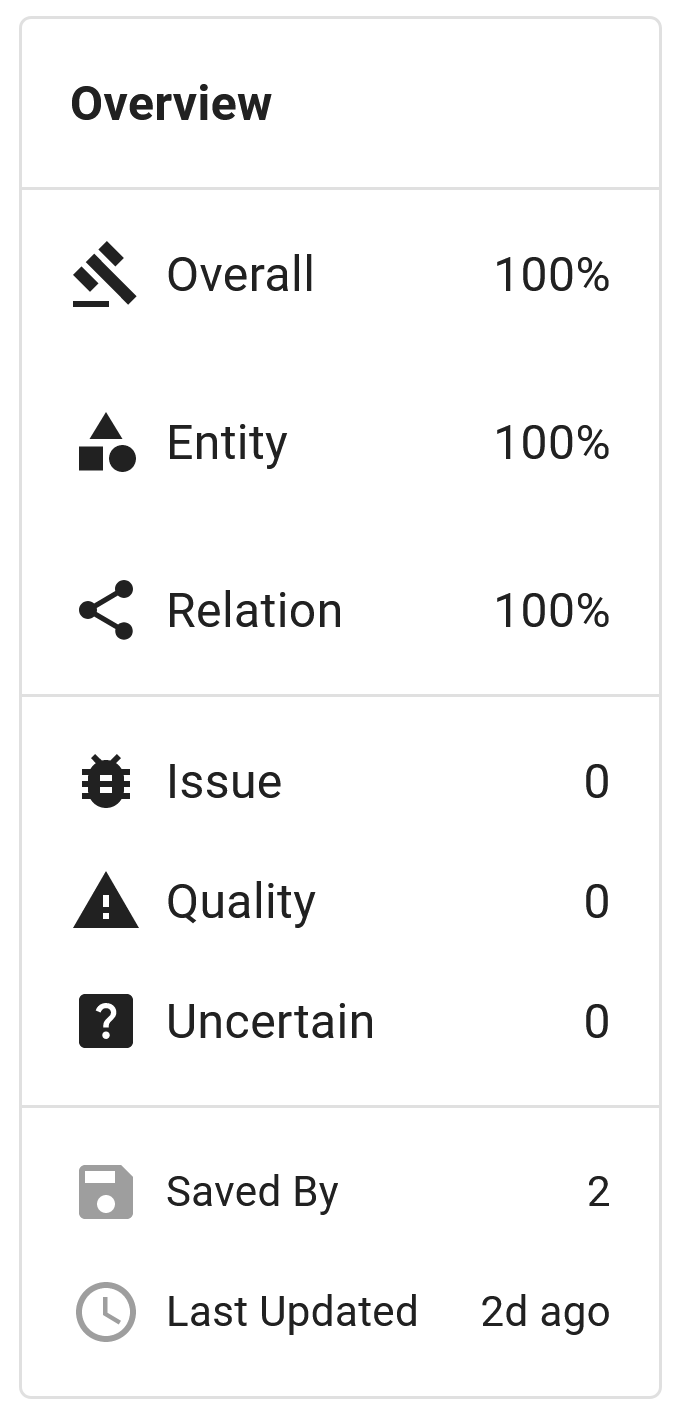
The adjudication overview (Figure 3) presents a concise summary of key information about the dataset item, including agreement measures, flag status, save status, and the last updated timestamp.
For projects involving both entity and relation annotation, the overview displays the overall, entity and relation agreements scores. Otherwise only the overall agreement score is presented. The 'flags' section shows the count of annotators who have assigned the flags issue, quality, or uncertain. By hovering over the flag count, you can view the usernames of the annotators who have flagged the item. The bottom of the overview shows the number of annotators that have saved the dataset item. Like with flags, hovering over the count will reveal annotators' names. Lastly, the overview provides information on when the dataset item was last updated to help track the item's progress.
3. Main View and Annotator Selector
The primary section of the adjudication tab comprises two integral components: the Main View and the Annotator Selector.
The Main View showcases applied entities, relations (for projects designated as entity and relation annotation), and comments associated with the dataset item.
The Annotator Selector, depicted in Figure 4, offers dynamic viewing options. Choosing overview reveals entities and relations that share majority agreement among all annotators. Selecting a single annotator displays their unique annotations, whereas picking a pair of annotators exhibits the degree of agreement between their annotations. This functionality provides swift and clear insight into the alignment of annotators' contributions.
The 'Relations' section presents applied relations in a triplet format (source)-[relation]->(target). More information about the source, relation, or target, such as their respective labels, can be seen by hovering over them.